In free - form optics, the optical devices have surfaces that lack rotational symmetry or translational symmetry around the optical axis. These are refractive and reflective surfaces, which differ significantly from the geometric shapes of traditional spherical and aspherical surfaces. When manufacturing free - form optical components, it is first necessary to precisely define the surface, and the mathematical representation is highly demanding and complex.
The mathematical description of aspheres is based on the ISO 10110 standard and calculated using the Zernike - Fringe polynomial. The mathematical representation of the surface profile is as follows:
z=1+1−(k+1)c2r2cr2+∑i=1nAiZi(r,ρ,φ)
where c is the reciprocal of the radius of curvature, k is the conic constant, Zi is the standard Zernike polynomial, Ai is the Zernike coefficient, r is the radial coordinate of the surface, ρ is the normalized radial coordinate, and φ is the angular coordinate.

Comparison of Spherical, Aspherical, and Free - Form Surfaces in Terms of Field of View (FOV), Numerical Aperture (NA), and Miniaturization
High Degrees of Freedom: Compared with spherical or aspherical surfaces, free - form surfaces have more degrees of freedom. They break the limitations of traditional symmetry, offering more possibilities for optical system design. This makes the geometric shapes of optical components more complex. At the same time, reference structures are required for orientation.
Performance Improvement Advantages: It shows excellent performance in terms of the field of view (FOV), numerical aperture (NA), and miniaturization, and can freely optimize and improve these three parameters.
Unique Functions: With its special surface shape, it can achieve functions that traditional optical devices cannot. It is especially suitable for small - scale optical components, such as monolithic components. It has obvious advantages in folding the light path and can replace existing reflector systems. A single free - form optical component can save time on installation and alignment.
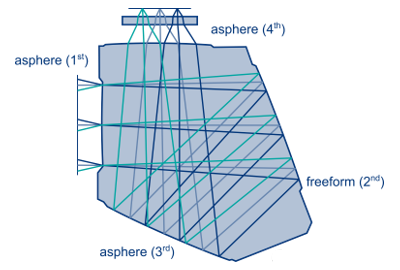
Optical Design of a Monolithic System Composed of Three Aspherical Surfaces and One Free - Form Surface
Automotive Industry: In the driver assistance system, more sensor systems are installed in vehicles to enhance the driving experience. Free - form optics allows each optical component to occupy less installation space. It is widely used in newer car models, such as in head - up displays.
Imaging/Display Industry: It is used in projection systems, etc., meeting the requirements of folding the light path, focusing obliquely incident light, and miniaturizing the system.
Safety Application Field: For example, in the helmet camera system for firefighters, free - form optics is used in thermal imaging. By combining an infrared camera with AR glasses, thermal images can be seen immediately, which is convenient for searching for trapped people in the ruins of buildings. This can replace traditional handheld infrared cameras.
Since free - form optics has relatively many geometric degrees of freedom, the parameter requirements for design and production are extremely strict. It is necessary to take into account more compact design, good optical performance, and system miniaturization. As more application possibilities emerge in the field of optics and new markets gradually open up, free - form optics will play an increasingly important role in the future.